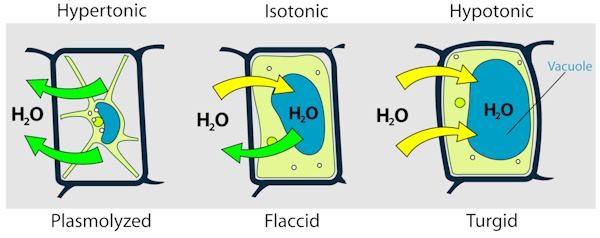
Potato cells contain water along with dissolved minerals and salts that help it stay firm and healthy. When a potato is placed in different surrounding solutions, water moves in or out of its cells depending on how concentrated those solutions are. This movement of water reveals important information about the internal environment of the potato.
In this activity, you will estimate the approximate concentration of the solution inside a potato using the process of osmosis. By placing potato strips in solutions of different concentrations and measuring how their mass changes, we can determine the point at which there is no net movement of water. That concentration will be closest to the natural salt and mineral concentration within the potato cells.